The acoustic trauma
The ear can be damaged by very violent sounds , which can lead to a loss of hearing.
Basically it distinguishes between a "chronic" acoustic trauma and an "acute" acoustic trauma.
The chronic acoustic trauma is a relatively common disease in occupational medicine and is due to exposure over long periods of time intensity sound sources above 85 dB.
An "acute acoustic trauma" is defined asan event that leads to a short exposure to sound waves with a very high energy, over 120 dB.
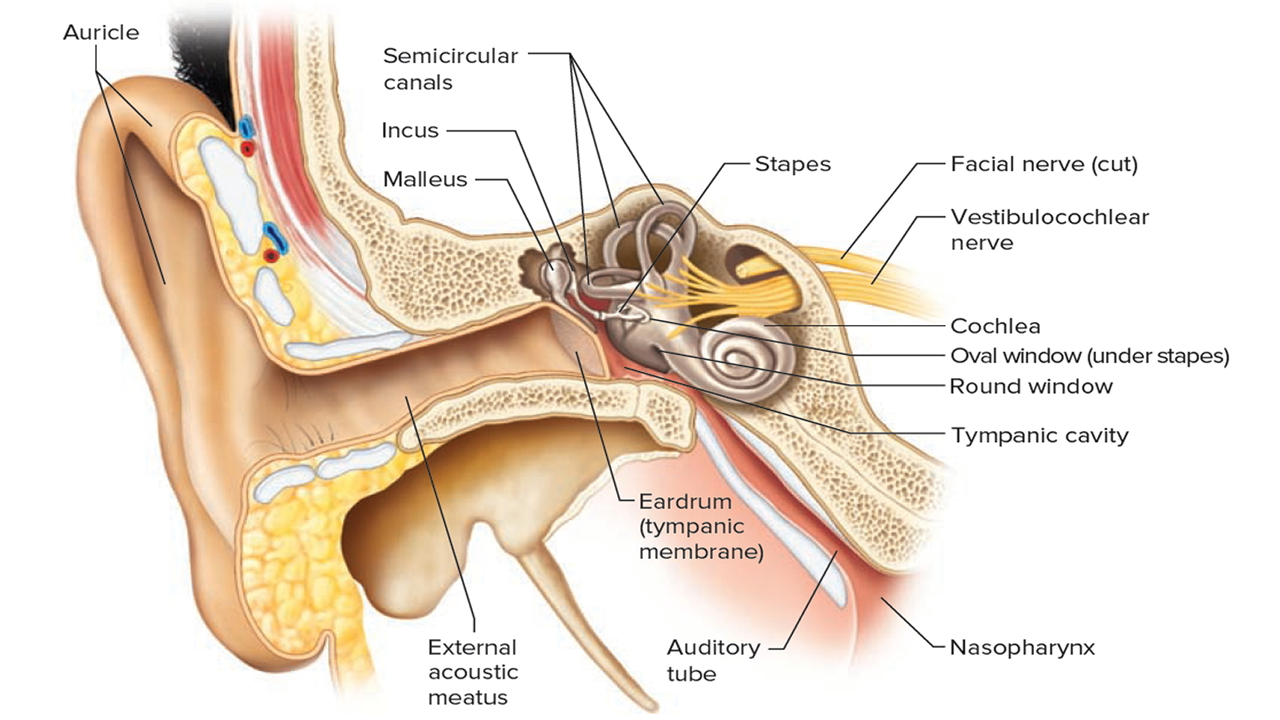
Sound waves are mechanical waves, like those of the sea.
To make a comparison we could say that a sound wave with an intensity of 120 db and above could be compared to a tsunami, a high and violent wave, which hits the delicate structures of the ear.
The violent impact can damage the mechanical part leading to tearing of the tympanic membrane, but more often occurs damage to the nervous structures where the internal ear fluid (perilinfa and endolymph) in turn generate a violent wave that tears and damages the auditory receptors.
For anatomical reasons, the violence of the perilinfatica wave is almost exclusively striking on the sector that conveys the frequencies of 4 and 6 kHz, which correspond to very acute sounds.

The acute acoustic trauma can arise following detonations, explosion of firecrackers and explosions in general.
Following the acoustic trauma in the affected ear immediately appears a strong whistle called tinnitus, which is associated with a feeling of ovulation of the ear and loss of hearing . Generally it is advisable to wait at least a few hours before becoming alarmed.
In fact, if the acoustic energy at stake was sufficient to damage the ear but not permanently, within a few hours you should see the whistle drop and the hearing resume.
This picture, well known to children who go to the disco and come home deaf, but after sleeping wake up without more disturbances, configures the so-called TTS, an English acronym meaning Temporary Threshold Shift , that is "temporary modification of the hearing threshold ".
In cases in which more than 24 hours have passed, the symptoms do not show any improvement, so contact immediately with an ENT specialist.
Probably this is a more serious damage, called PTS, that is Permanent Threshold Shift.
In this case it is necessary to start medical treatment as soon as possible, sometimes with home medicines.
Sometimes the damage to the ear is particularly severe and the ENT specialist decides for immediate hospitalization with the execution of an infusional drug therapy.